-
[ 데이터통신 ] chapter 5. Analog Transmission전공공부/데이터통신 2021. 4. 16. 20:43
안녕하세요. 개알못입니다~~
이번 포스터는 데이터통신 과목에서 Analog transmission 에 관하여 다루겠습니다.
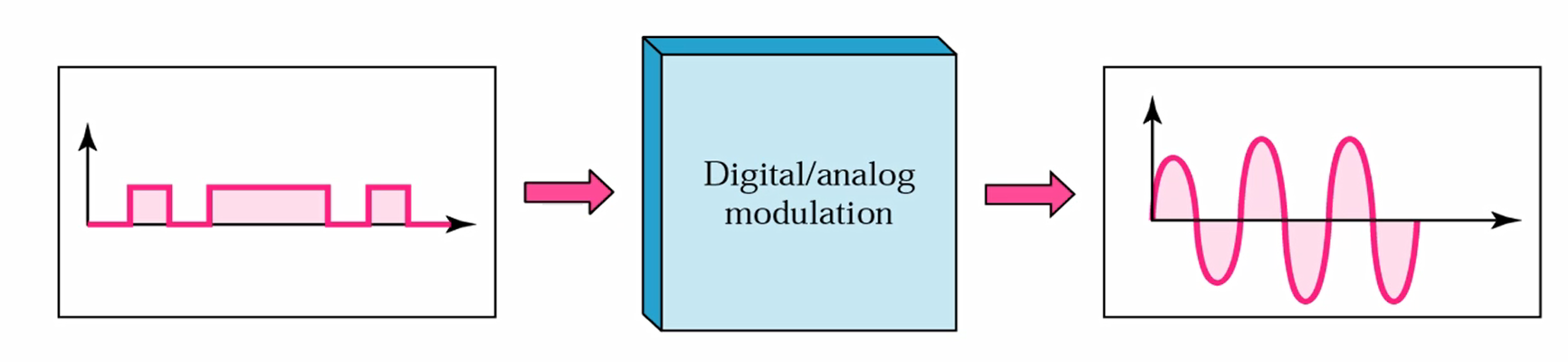
5.1 Modulation of Digital Data
- Modulation
Converting binary data or a low-pass anlalog signal to a band-pass analog signal
Characteristics ofs a sine wave : Amplitude, frequency, phase
- Bit rate vs baud rate
Bit rate : bits transmitted during one second
Baud rate : signal units per second = bit rate x bits represented by a signal unit
Baud rate is less than or equal to the bit rate
- Carrier signal
A high-frequency signal that acts as a basis for the information signal in an analog transmission.
Digital information modulates the carrier signal by modifying one or more of its characteristics.
- ASK (Amplitude Shift Keying)

Change the strength of a carrier signal
Highly susceptible to noise ( Problematic for ASK)
On/off keying
Bandwidth = (1+d) x N (d : a factor related to the modulation process)
- FSK (Frequency Shift Keying)

Change the frequency of a carrier signal
Avoid the problems from noise
Limiting factor : physical capability of a carrier
Bandwideth = Fc1 - Fc0 + N
- PSK (Phase Shift Keying)

the phase of the carrier is vared
Peak amplitude and frequency remain constant
Not susceptible to noise : reliable detection
No bandwidth limit problem as in FSK
Bandwidth : same with ASK
Usually higher bit rates than ASK
2PSK or binary PSK (the same rate as ASK)
4PSK, QPSK : dibit
8PSK : tribit
- QAM (Quadrature Amplitude Modulation)
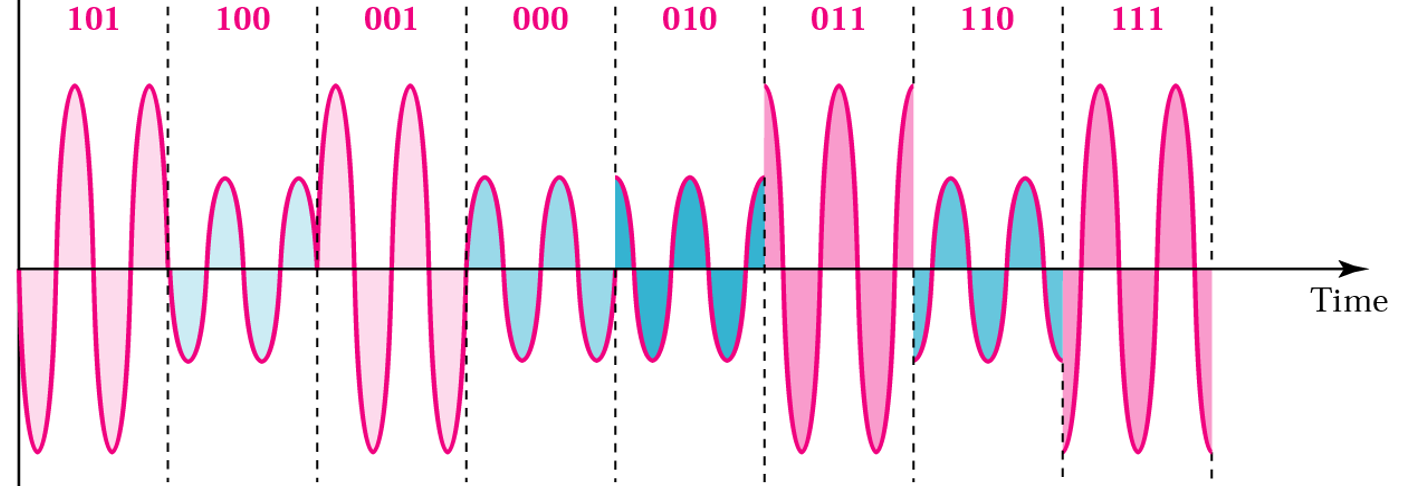
A combination of ASK and PSK
A maximum contrast between each signal unit
5.2 Telephone Modems

- A telephone line has a bandwidth of almost 2400 Hz for data transmission.
- Modems stands for modulaot/ demodulator.
5.3 Modulation of Analog Signal
- Analog-to-analog modulation
- Amplitude Modulation (AM)
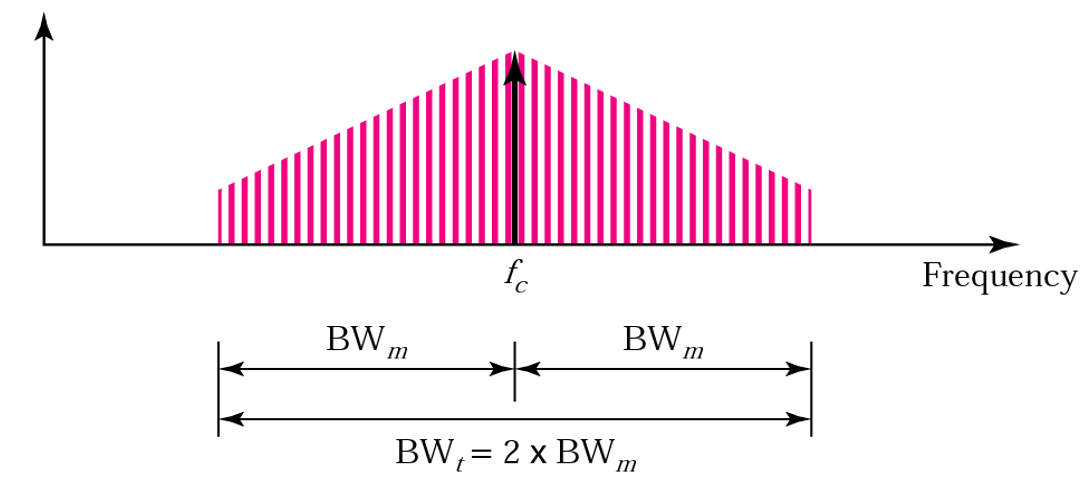
The total bandwidth required for AM can be determined from the bandwidth of the audio signal
BWt = 2 x BWm
- Frequency Modulation (FM)

The total bandwidth required for FM can be determined from the bandwidth of the audio signal.
BWt = 10 x BWm
참고자료 : Data Communications and Networks, fourth edition by Behrouz A, Forouzan
혼자 공부 중에 정리한 것이니, 질문이나 추가할 부분이 있으시면 댓글 달아주세요 :)
'전공공부 > 데이터통신' 카테고리의 다른 글
[ 데이터통신 ] chapter 6. Multiplexing (0) 2021.04.16 [ 데이터통신 ] chapter 4. Digital Transmission (0) 2021.04.15 [ 데이터통신 ] chapter 3. Signals (0) 2021.04.14