-
[ 데이터통신 ] chapter 3. Signals전공공부/데이터통신 2021. 4. 14. 22:25
안녕하세요. 개알못입니다~~
이번 포스터는 데이터통신 과목에서 Signal에 관하여 다루겠습니다.
- To be transmitted, data must be transformed to electromagnetic signals
3.1) Analog and Digital
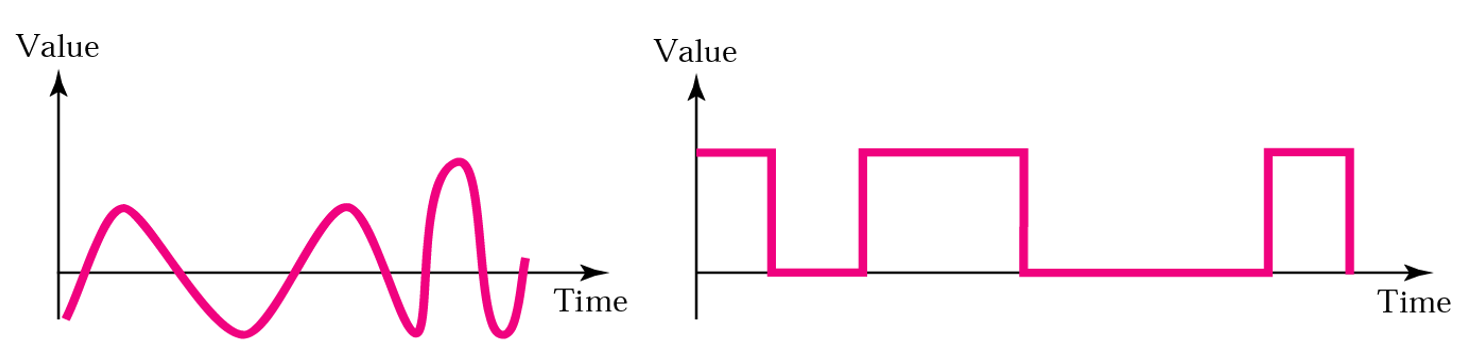
- Signals can be analog or digital
- Analog signals은 무한한 값 (infinite)
- digital signals은 유한한 값 (limited)
- 보통 아날로그 신호는 주기(periodic), 디지털 신호는 비주기 (aperiodic)
- 아날로그 주기는 어떤 신호라도 주기 신호복합체로 나타낼 수 있다.
3.2) Analog Signals


- Analog Signal
정현파는 최대 진폭, 주파수, 위상에 특성을 가짐
주기와 주파수는 서로 역관계
주파수란 1초 동안 생성되는 신호 주기의 수 = Frequency is the rate of change with respect to time.
위상이란 시각 0시에 대해 파형의 상대적인 위치 = Phase describes the position of the waveform relative to time zero.
[cycle] x 360 = [degrees]
[degrees] x 2pi/360 = [radians]
An analog signal is best represented in the frequency domain
A Single-frequency sine wave is not useful in data-communications. So we need to change one or more of its characteristics to make it useful => it becomes a composite signal made of many frequencies.
푸리에 해석에 따르면 임의의 복합 신호는 서로 다른 주파수, 진폭, 위상을 갖는 단순 정현파(sine wave)들의 조합으로 나타낼 수 있다.
- Square wave
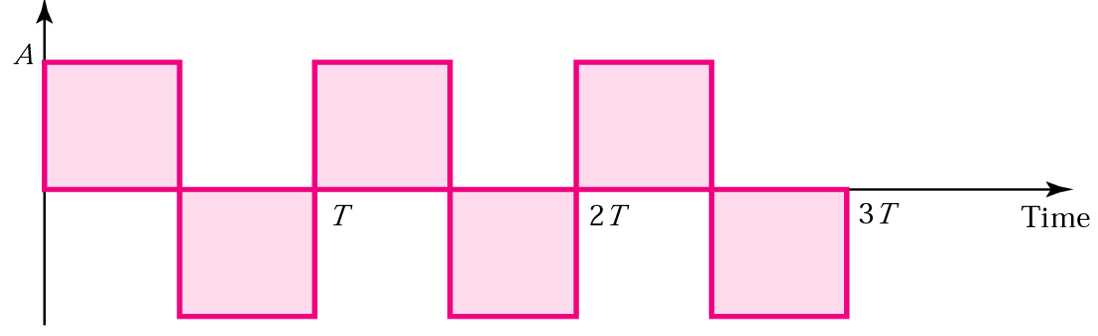

Fundamental Frequency : f
harmonics : 3f, 5f
Frequency spectrum : all frequency. componets
Composite signal
- A medium may pass some frequencies and may block or weaken others
- Bandwidth
복합 신호에 포함된 주파수 영역
복합 신호의 대역폭은 신호에 포함된 최고 주파수와 최저 주파수의 차이
Normally the range of frequencies that a medium can pass without losing one-half of the power in that signal.
The relationship between bandwidth of a medium and bandwidth of a signal. If they does not match, some of the frequencies are lost.
3.3) Digital Signals

- Bit interval instead of period in analog signals = time for sending a single bit
- Bit rate instead of frequency = number of bit intervals per second (bps)
- A digital signal is a composite signal with an infinite bandwidth
- 디지털 신호는 기본적으로 wide-Bandwidth Medium에서 해야한다.
- 디지털 신호가 Band-Limited Medium에서도 될 수 있다. 그러나there exists the relationship between the number of bps and the minimum required bandwidth. => the Nyquist theorem, the Shannon capacity
- the bps and the required B/W using only more harmonic => B = n/2 + 3n/2 + 5n/2 + ....
- B>=n/2 or n<=2B
- The bit rate and the bandwidth are proportional to each other.
- Digital bandwidth for digital data(bps) = Maximum bit rate through a medium can pass
- Analog bandwidth for analog data(hz) = Range of frequencies that a medium can pass
3.4) Analog versus Digital
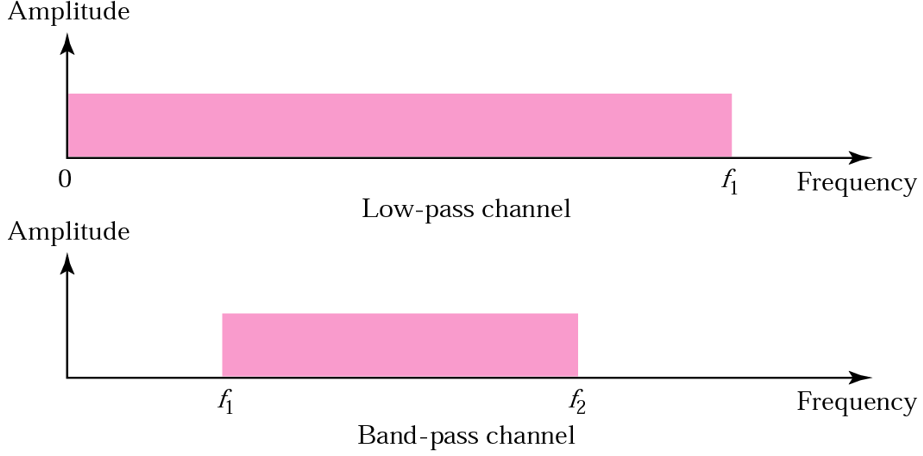
- A low-pass channel has a BW with frequencies between 0 and f.
- A band-pass channel has a BW with frequencies between f1 and f2.
- Digital transmission needs a low-pass channel.
- A low-pass channel only if the medium is dedicated two devices(point-to-point) or shared between several devices in time(not in frequency).
- Analog transmission can use a bane-pass channel. this is not to say that an analog transmission cannot use a low-pass channel.
- Advantage : a band-pass channel is more available
The BW of a medium can be divided into several band-pass channels to carry several analog transmissions instead of one digital transmission. ex) in analog cellular telephony, a limited bandwidth is divided between many users.
3.5) Data Rate Limits
- Data rate depends on
The bandwidth available
The levels of signals we can use
The quality of the channel ( the level of the noise )
- Noiseless channel : Niquist bit rate
BitRate in bps = 2 x bandwidth x log2L (L : number of signal levels)
- Noisy channel : Shannon capacity
Capacity in bps = bandwidth x log2(1 + SNR)
we cannot a data rate higher than the capacity of the channel of the channel, irrespective of the levels of the signals.
3.6) Transmission Impairment
- Attenuation(감쇠), Distortion(일그러짐), Noise(잡음)
- Attenuation
Loss of energy due to the resistance of the medium.
To compensate for this loss, amplifiers are used.
- Decibel
dB = 10log10(P2/P1)
positive value : the signal has been amplified(증폭)
negative value : the signal has been attenuated(감쇠)
- Distortion : the signal changes its form or shape
occurs in a composite signal.
Because each signal has its own propagation speed through a medium.
- Noise
Thermal noise : Random motions of electrons (열잡음)
Induced noise : form motors and appliances ( 유도된 잡음)
Crosstalk : Noise from other wires as antenna (혼선)
Impulse noise : Spike noise from power lines, lightning (충격 잡음)
참고자료 : Data Communications and Networks, fourth edition by Behrouz A, Forouzan
혼자 공부 중에 정리한 것이니, 질문이나 추가할 부분이 있으시면 댓글 달아주세요 :)
'전공공부 > 데이터통신' 카테고리의 다른 글
[ 데이터통신 ] chapter 6. Multiplexing (0) 2021.04.16 [ 데이터통신 ] chapter 5. Analog Transmission (0) 2021.04.16 [ 데이터통신 ] chapter 4. Digital Transmission (0) 2021.04.15